The Power of Pork Protein
Pork Nutrition
Pork is naturally low in sodium and a “good” source of potassium — two nutrients that, together, can help regulate blood pressure.
Both the pork tenderloin and pork sirloin roast meet the criteria for the American Heart Association Heart Checkmark, which means they contain less than 5 grams of fat, 2 grams or less of saturated fat, and 480 milligrams or less of sodium per label serving. Pork is also packed with protein, making it easy to include in a health-forward and balanced diet.
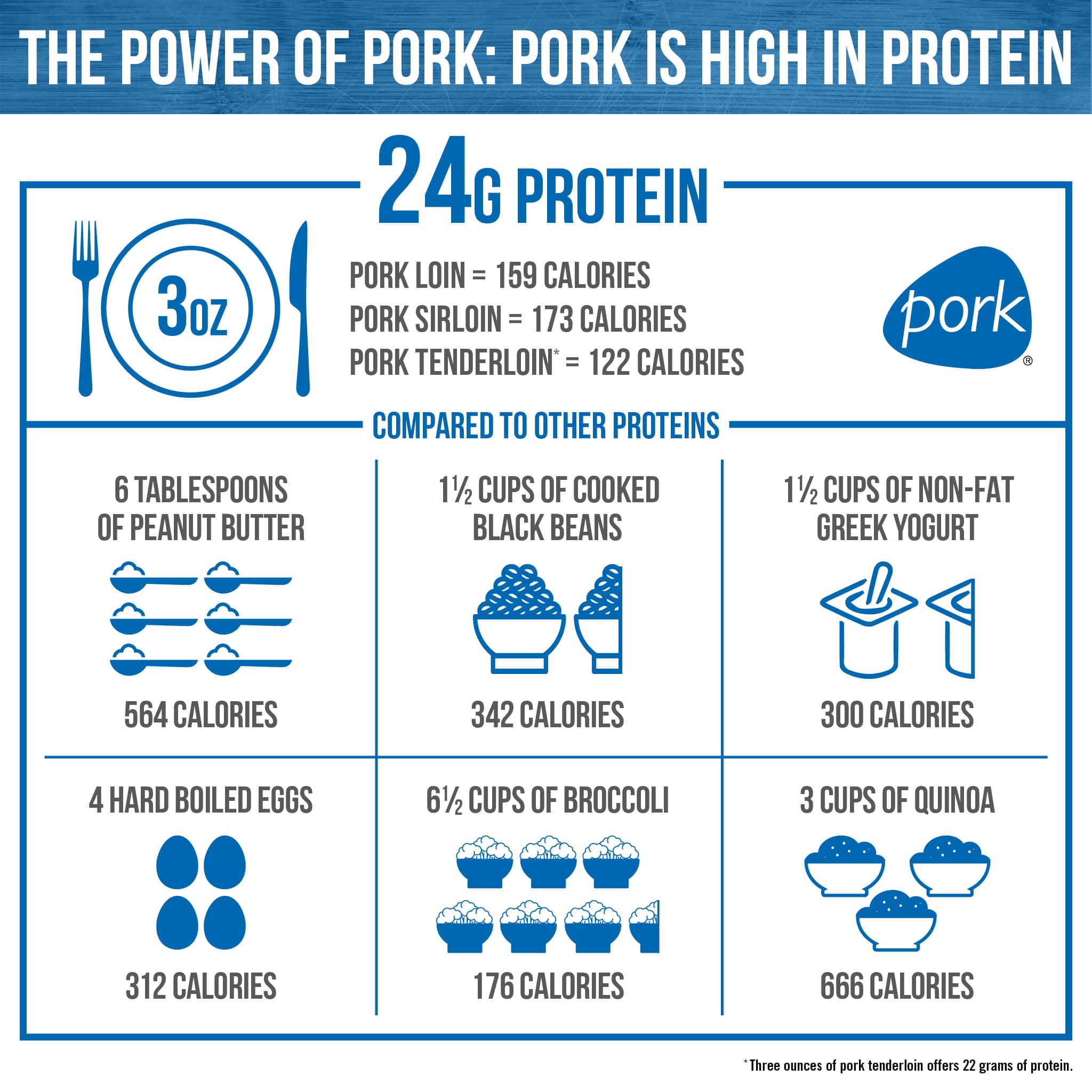
How much protein is in pork?
- Per 3 oz serving -
How much protein do you need?
The Institute of Medicine suggests that about 10-35% of your day’s total daily calories should come from protein; and of that protein, they recommend about 20 to 30 grams per meal to help maintain muscle mass and function.
Bonus: eating twice the recommended amount of protein has been linked to beneficial effects on muscle and body composition, leg power, weight loss, weight management, and healthy aging.
Meal and Fitness Plans
Minnesota Pork partnered with 3 Minnesota brands to bring you a FREE 4-Week Meal Plan + Workout Challenge: Minnesota Beef, The Real Food Dietitians, and Nourish, Move, Love.
Nutrition Resources
Pork is packed with protein, making it easy to include in a health-forward and balanced diet. It has many beneficial qualities including its versatility and nutrient profile that make it easy to incorporate into a healthy lifestyle.
Sort by:
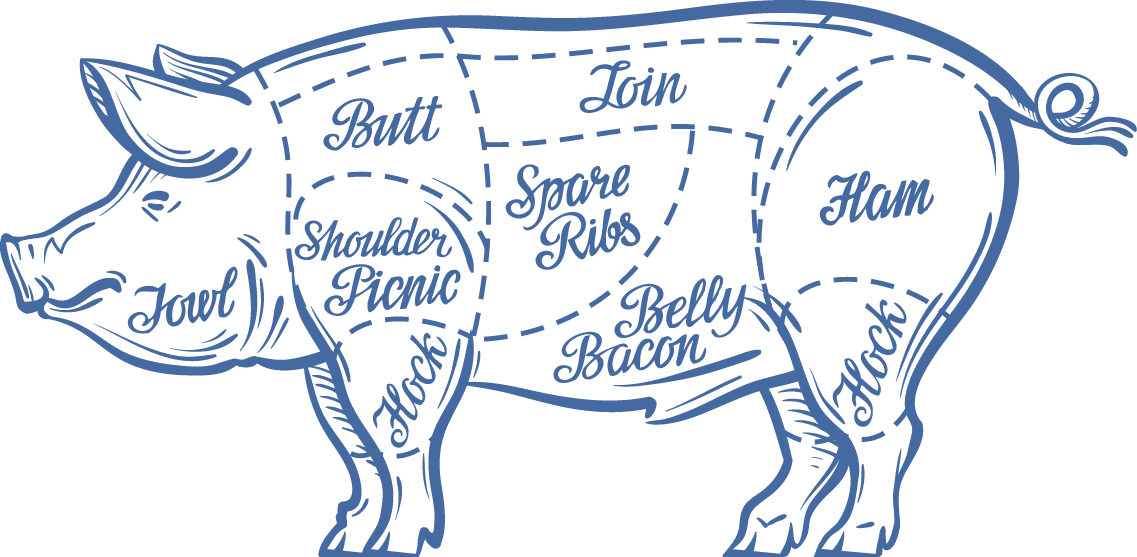
Looking for lean cuts of pork?
Pork cuts with the word “loin” or “chop” in the name are low in fat and high in protein.
- Pork Tenderloin
- Sirloin Pork Chop
- Sirloin Pork Roast
- New York Pork Chop
- Porterhouse Pork Chop
- Pork Loin Roast
All of the Goodness
of Pork
What nutrients does Pork contain?
Releases energy from foods
Maintains healthy skin
Maintains the digestive track
Protects the nervous system
Enhances and protects bones
Improves resistance to infection
Helps from hormones & enzymes
Develops & maintains immune system
Supplies energy
Protects & insulates body parts
Nourishes skin
Transports vitmains A, D, E, and K
Supplies essential fatty acids
Builds and repairs body tissues
Regulates body processes
Forms antibodies to fight off infection
Releases energy from proteins
Maintains the nervous system
Builds & repairs body tissues
Maintain healthy skin & eyes
Releases energy from proteins
Helps transport amino acids
helps form niacin (Vitamin B3)
Aid in the functioning of the nervous system
Releases energy from foods
Forms cholesterol, hormones, and hemoglobin
Builds and repairs nerves and muscles
Maintains an appetite
Releases energy from carbohydrates
Maintains red blood cells
Ensures healthy nerve tissue
Helps produce genetic material
Supports cell function and metabolism
Builds hemoglobin in red blood cells
Prevents nutritional anemia
Helps with energy production